Biocellulose
a.k.a. biosynthesized cellulose, bacterial cellulose, is a natural biopolymer used in medicine, biotechnology, pharmacy or cosmetology, attracted considerable attention of global R&D leaders.
Bacterial cellulose is obtained by fermentation, using non-pathogenic bacteria Komagataeibacter xylinus E25. This biopolymer consists of a regular, densely woven network of nanofibers, forming a three-dimensional structure similar to the extracellular matrix of human tissue.
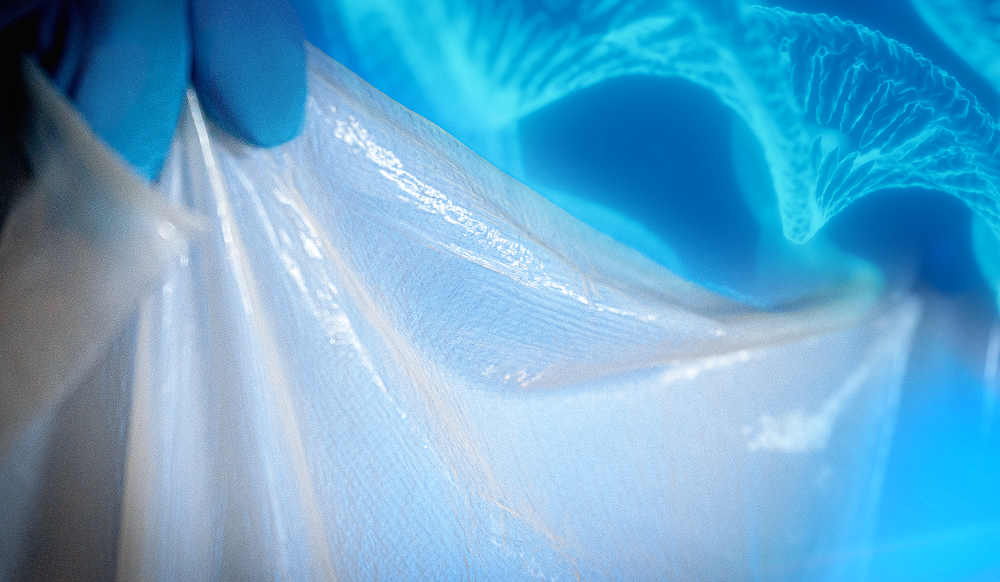
Biocellulose fiber diameter is below 100nm, ultrapure biomaterial has unique physical and chemical properties, such as water-binding capacity, tensile strength, low thrombogenicity and no toxicity.
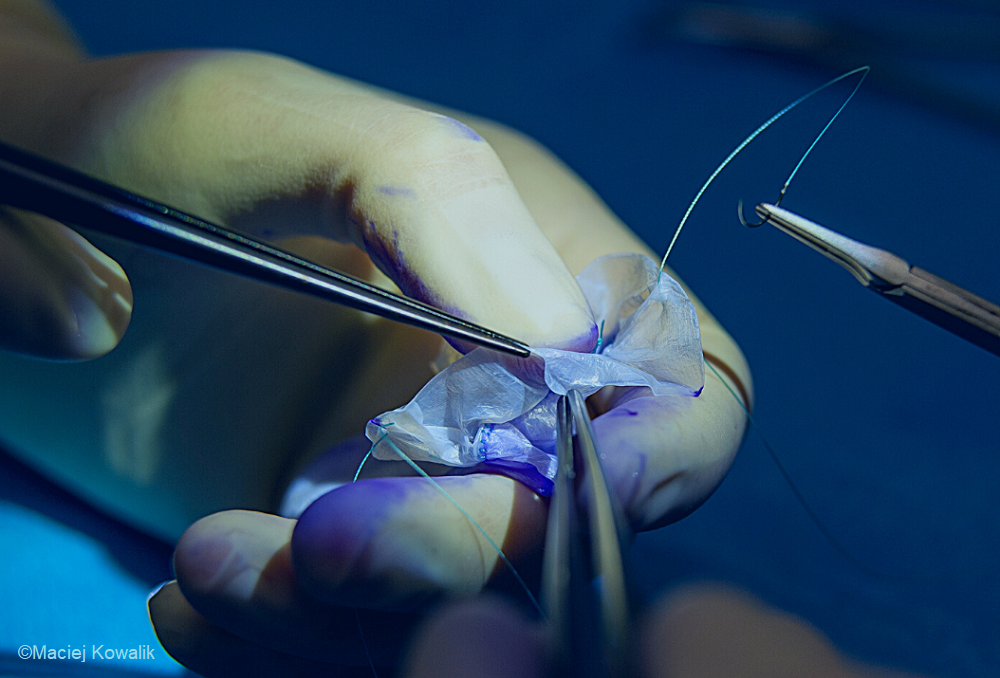
The advanced and fully controlled biotechnological production of bacterial cellulose, leads to a reproducible and uniform product. The biocellulose complies with standards for biomaterials and has an excellent features as a human soft tissue repair material. The bacterial cellulose adapts perfectly to irregular anatomical contours, works well in contact with human blood, so it can be used to prosthetic blood vessels or elements of the cardiovascular system.

BC various applications
Over recent years, biosynthesized cellulose has received attention of experts and physicians, who find its application in medicine, biotechnology, pharmacy or cosmetology:
- cardiac surgery (blood vessels, pericardial patches)
- diabetology (dressings for venous ulcers and diabetic foot)
- pharmacy (drug delivery systems)
- orthopedics (cartilage tissue implants, meniscus)
- neurology (dura implants)
- ophthalmology (cornea implants)